Space is really awesome, and so are the ways we can get to space! So lets understand how the rocket parts work because even if you won’t get a degree in rocket science, its still good knowledge!
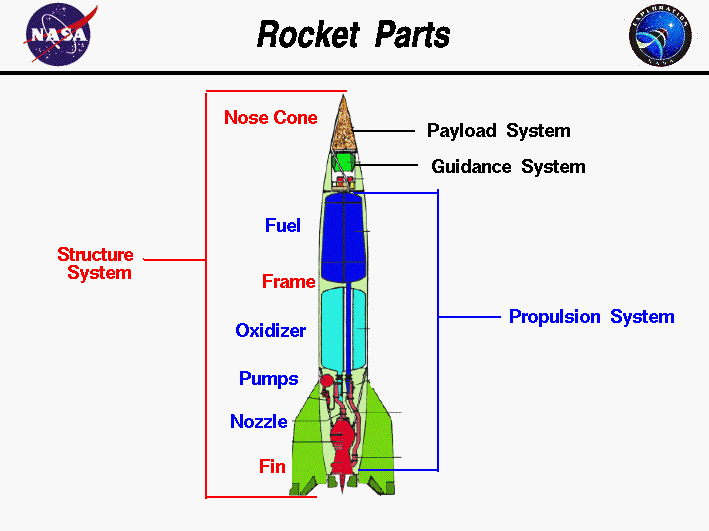
The cone at the very top of a rocket is the nose cone. It protects the payload during launch and reduces air resistance. That means that air particles collide with the rocket, and moves the opposite direction from the rocket, pushing it down. The nose cone reduces that resistance.
The next part is the payload and body tube. The payload carries cargo, like satellites and objects for space exploration. The body tube carries other important systems like the propulsion system (we’ll get to that later).
The guidance system controls the rockets direction using accelerometers and gyroscope sensors. The fuel tanks store propellant. This liquid is very dangerous, which is why it is stored in a tank. Oxidizer tanks store oxygen, which is not available in space. This is important for burning propellant. Avionics are the computer systems that monitor the rocket.
Then, fins help the rocket stay stable and maintain direction, like a fish. The most important part is the engine, which gives the rocket thrust, or energy to move upwards, like how a car engine helps a car move forward. Finally, at the end, the recovery system includes a parachute so the rocket can safely return to earth without harming Earth or the rocket.
Propulsion System
The propulsion system is basically the engine and thrust, but I will explain a more direct version.
Propellant is the fuel in a rocket. Without propellant, the rocket would not be able to lift and move. The combustion chamber is where the propellant is burned. This is kinetic energy. The propellant is converted into a usable form, or gas. The nozzle is the part at the bottom where the gas is let out. Because of so much energy, the rocket gets thrust and lifts the rocket!
Turbopumps work like the name suggests; it quickly pumps propellant into the combustion chamber. This job has to be quickly done in order for the rocket to keep moving. Ablative cooling is for the combustion chamber. High amounts of heat and energy are produced in that part, so the ablative cooling protects the walls.
Rocket Materials
One important thing about rockets is that they do not use a lot of metal because it is very heavy. So instead, they use aluminum, which is lighter and stronger. Scientists have to analyze the materials to make sure they are strong enough to handle the stresses of launch, and light enough to even be able to launch.
Navigation
I get lost in my own neiborhood, so how do rockets know their way in space?? Well, they use many systems. GPS provides exact location, actuators control the rockets direction and orientation, and inertial measurement unit measures acceleration and rotation rates!
Separation Systems
Because after the rocket enters space, some items are unnecessary to take, like the booster engines, which give the thrust to enter space. So, the parts are separated by the separation system. Some popular systems are the Pyrotechnic devices, Pneumatic devices, and the Linear shaped charges. The Pyrotechnic devices use small, explosive charges and are efficient, but do leave debris. The Pneumatic devices use high pressure gas to pull parts apart and are clean, but need gas tanks and are hard to store. Finally, the LSC (Linear shaped charges) use explosives for precise separation clean and efficiently, but are very complicated to make.